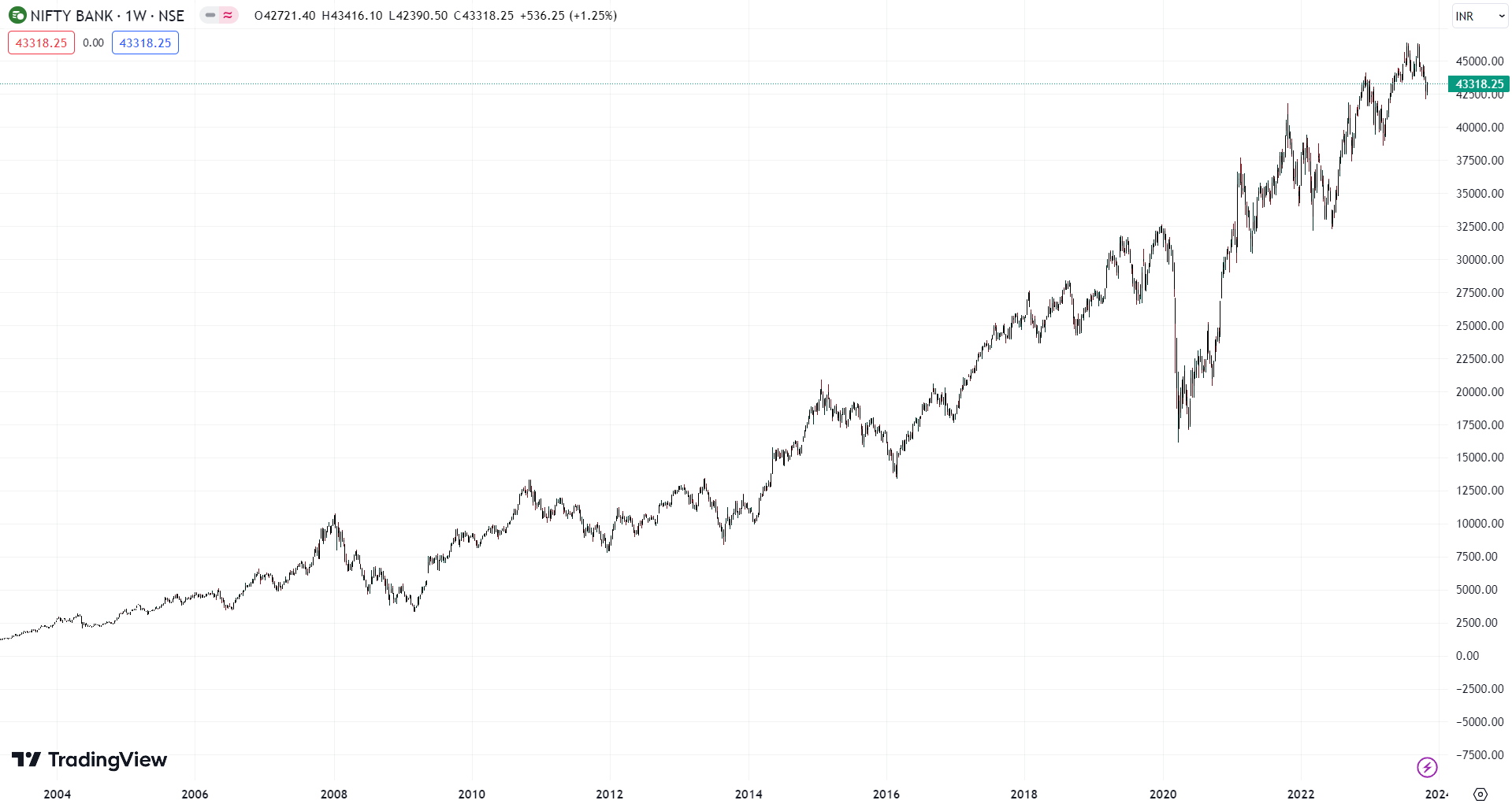
The stock market index that monitors the performance of India’s banking industry is called BANKNIFTY. It was created in 2023 by the National Stock Exchange (NSE) to allow for the free movement of the capital market performance of banking, one of India’s most important service sectors. There are twelve banks in the index, both private and state-owned. Those are bullish on banks can go long or buy call option of Bank Nifty or can also buy the future of Bank Nifty. Bears can also short or sell the Bank Nifty call option if they are bearish in the Bank Nifty or can also short the future of Bank Nifty. The Bank Nifty is high volatile than the nifty 50 futures. Since it was established in 2003, the Bank NIFTY has served as a helpful benchmark for institutional and retail investors investing in banking stocks.
HOW THE BANK NIFTY INDEX WORKS?
If you want to use the Bank NIFTY index as a benchmark for your stock selections, you should understand how it operates. Whether your goal is to invest in direct equities, mutual funds, or an imminent initial public offering (IPO) in the banking industry, Bank NIFTY can assist you in assessing the potential returns on your investment. Due to the weighted nature of this index, both individual investors and market intermediaries can make well-informed decisions. Investors may see the capital market performance of the banking sector clearly thanks to the index.
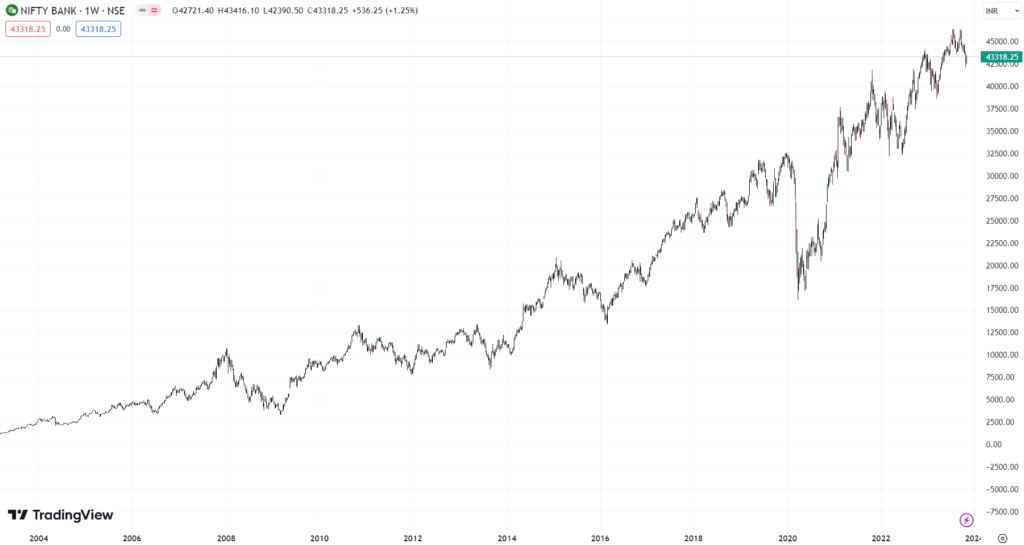
There are various reasons why the Bank NIFTY index is frequently mentioned. It works well, for example, when benchmarking fund portfolios, introducing new exchange-traded funds (ETFs), learning about other index funds, and comprehending more complex financial products. Despite its 2003 launch, this index uses 2000 as its base year. Real-time values and prices for Bank NIFTY stocks are displayed during regular National Stock Exchange trading hours.
The following are a few major takeaways on how the Bank NIFTY operates:
The Index as a Benchmark
Mutual fund managers and investors frequently utilise the Bank NIFTY as a benchmark. When used as a performance benchmark, it provides investors with information about the overall performance of banking companies as well as the likelihood of gains for specific funds. Investors’ primary argument for utilising Bank NIFTY as a good benchmark is to outperform Bank NIFTY returns. So, if a fund generates returns above those of the Bank NIFTY index, you might consider that fund to be a wise investment.
Let’s say a manager of a mutual fund has bought equities in banks. Furthermore, suppose that in a specific year, 2020, these generated returns of 18%. Let us assume that in 2020 the Bank NIFTY yields a 20% return. The fund in question hasn’t been able to beat the Bank NIFTY index in this situation. The mutual fund would have outperformed the index if it had generated returns equal to 23 percent. This index is typically used by mutual fund professionals and individual investors to assess the performance of their investments.
The BANK NIFTY for OPTION TRADING
Now that you are aware of what NIFTY Bank is, you should be able to understand how investors and other financial experts use it. Trading options within the index is another application for this index. Typically, the index yields returns between 2% and 3%. In light of this, investors can use a variety of techniques while trading Bank NIFTY options.
BANKNIFTY 12 COMPANIES
| SN | Bank | Weightage in % |
| 1 | HDFC Bank | 29.01% |
| 2 | ICICI Bank | 23.14% |
| 3 | Axis Bank | 9.98% |
| 4 | State Bank of India | 9.83% |
| 5 | Kotak Mahindra Bank | 9.61% |
| 6 | IndusInd Bank | 6.25% |
| 7 | Bank of Baroda | 2.67% |
| 8 | Federal Bank | 2.32% |
| 9 | AU Small Finance Bank | 2.30% |
| 10 | IDFC First Bank | 2.02% |
| 11 | Punjab National Bank | 1.60% |
| 12 | IDFC First Bank | 1.25% |





